The European Union (EU) is a diverse conglomerate of nations, each with its own tax policies and economic structures. Understanding which countries contribute the most to income tax within the EU provides insight into the economic landscape and fiscal health of the region. This article delves into the top contributors and breaks down the highest tax-paying nations in the EU.
Top Contributors to Income Tax in the European Union
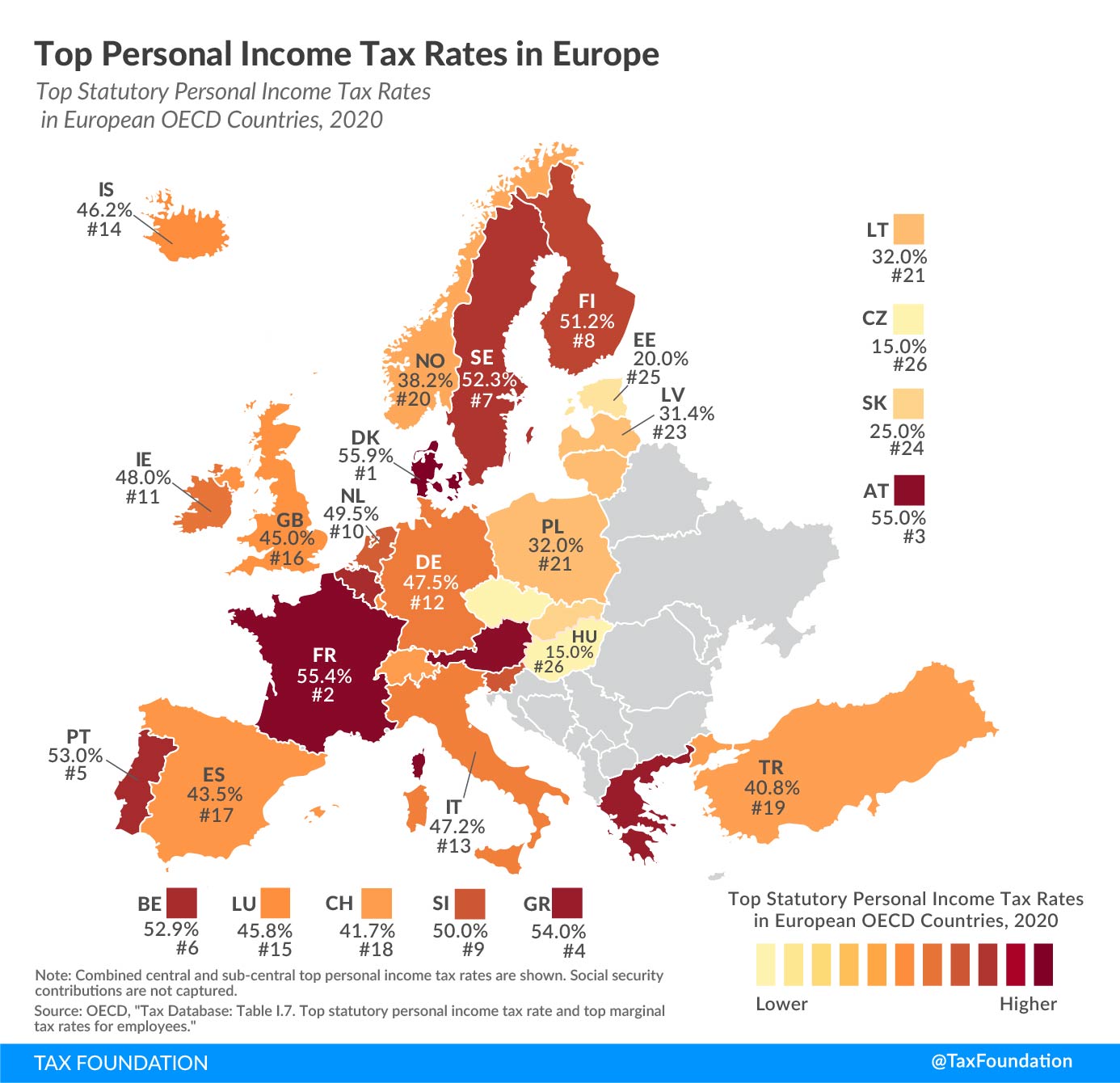
When discussing income tax contributions in the European Union, it is essential to recognize that larger economies naturally contribute more due to their substantial tax bases. Germany stands out as the top contributor to income tax in the EU. With the largest economy in Europe, Germany’s robust industrial sector, high employment rates, and progressive tax system ensure significant revenue from personal and corporate income taxes. The German government efficiently utilizes these funds to support a comprehensive welfare state, which includes extensive healthcare, education, and social security systems.
Following Germany, France is another significant contributor to the EU’s income tax revenue. France’s tax system is characterized by high tax rates, particularly for high-income earners, which helps generate a substantial portion of the nation’s revenue. The French government employs these funds to maintain its extensive social programs, including universal healthcare, pensions, and public services. The country’s commitment to social welfare is mirrored in its tax policies, ensuring a steady stream of income tax revenue.
Italy rounds out the top three contributors, despite facing economic challenges over the past decade. The Italian tax system is progressive, with higher earners paying a larger percentage of their income in taxes. While Italy’s economy is smaller than Germany’s and France’s, its sizeable population and significant industrial base contribute to its high income tax revenue. The Italian government allocates these funds to various public services, including healthcare, education, and infrastructure development.
A Breakdown of the Highest Tax-Paying Nations in the EU
Germany, as the EU’s largest economy, naturally leads in income tax contributions. The country has a tiered tax system wherein higher income brackets are taxed at progressively higher rates. This system ensures that wealthier individuals contribute a more significant portion of their income to the national revenue. Additionally, Germany’s corporate tax policies are designed to capture substantial revenue from its thriving industrial sector, further bolstering its position as the top tax-paying nation in the EU.
France’s tax structure is similarly progressive, with high-income individuals facing substantial tax rates. The French government has implemented various tax policies aimed at reducing income inequality and funding social welfare programs. Wealth taxes and social contributions are significant components of France’s tax system, ensuring that high earners and corporations contribute a fair share to the national budget. This approach not only supports the country’s extensive welfare state but also positions France as a leading contributor to the EU’s income tax revenue.
Italy, while facing economic difficulties, remains a key player in the EU’s tax landscape. The country’s progressive tax system ensures that higher earners contribute more, which is crucial given Italy’s economic constraints. Despite challenges such as tax evasion and a high public debt ratio, Italy’s income tax revenue remains substantial. The government continues to focus on tax reforms and measures to improve compliance, aiming to enhance revenue collection and fiscal stability.
The analysis of income tax contributions within the European Union highlights the significant role played by its largest economies. Germany, France, and Italy collectively contribute a substantial portion of the EU’s income tax revenue, driven by their progressive tax systems and economic structures. Understanding these contributions offers valuable insights into the fiscal dynamics of the EU and underscores the importance of effective tax policies in supporting social welfare and economic stability.