Value-Added Tax (VAT) and customs duties are critical components of international trade within the European Union (EU). For businesses involved in importing and exporting goods, understanding these financial obligations is essential to ensure compliance and optimize costs. This article provides an analytical overview of VAT and customs duties in the EU, offering key insights for importers and exporters to navigate these complex regulatory landscapes effectively.
Understanding VAT in the EU: Key Points for Businesses
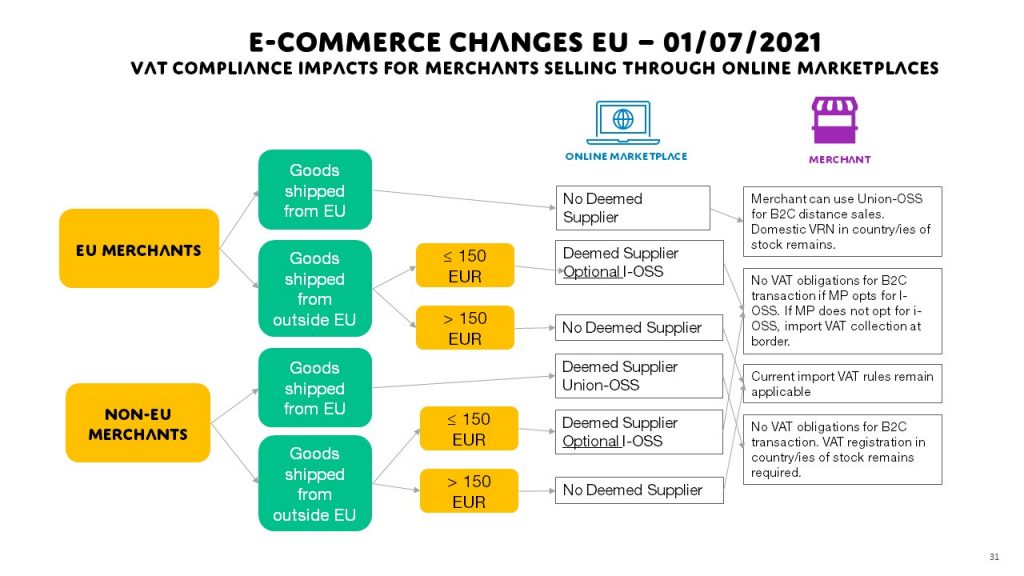
VAT is a consumption tax levied on the value added to goods and services at each stage of production or distribution. In the EU, VAT rates and regulations can vary significantly between member states, making it crucial for businesses to familiarize themselves with the specific requirements of each country they operate in. The standard VAT rate in the EU ranges from 17% in Luxembourg to 27% in Hungary, with reduced rates and exemptions applicable to certain goods and services. For importers and exporters, understanding these variations is vital for accurate pricing and compliance.
One of the primary considerations for businesses is the VAT registration threshold. Companies exceeding a certain turnover from sales within a particular EU member state must register for VAT in that country. This requirement can lead to multiple VAT registrations across different jurisdictions, adding to the administrative burden. However, the introduction of the EU VAT One-Stop Shop (OSS) scheme aims to simplify this process by allowing businesses to handle all their VAT obligations through a single registration and reporting system.
Another critical aspect is the reverse charge mechanism, which shifts the responsibility for paying VAT from the supplier to the customer in cross-border transactions within the EU. This mechanism aims to combat VAT fraud and reduce the administrative load on businesses. However, it requires a thorough understanding of the applicable rules and proper documentation to ensure compliance. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in significant penalties and disrupt business operations.
Navigating Customs Duties: Essential Insights for Traders
Customs duties are tariffs imposed on goods when they are transported across international borders. In the EU, these duties are governed by the Union Customs Code (UCC), which standardizes procedures across member states. The duty rates depend on the classification of goods under the Harmonized System (HS) and their origin. Importers must accurately classify their products to determine the applicable duty rates and ensure compliance with EU customs regulations.
One of the key challenges for traders is understanding the rules of origin, which determine the economic nationality of goods. These rules are crucial for benefiting from preferential tariff agreements that the EU has with various countries and regions. To qualify for reduced or zero duties under these agreements, businesses must provide proper documentation proving the origin of their products. Misclassification or incorrect documentation can lead to delays, additional costs, and potential penalties.
Additionally, the EU’s customs procedures involve various declarations and inspections to ensure compliance with safety, health, and environmental standards. Importers and exporters must be well-versed in the required documentation, such as the Single Administrative Document (SAD), and be prepared for potential inspections by customs authorities. Efficient customs management can significantly reduce clearance times and associated costs, enhancing the overall competitiveness of businesses in the international market.
Navigating VAT and customs duties in the EU can be complex, but with a thorough understanding of the regulations and proactive management, businesses can mitigate risks and optimize their operations. Staying informed about changes in legislation, leveraging available simplification schemes, and maintaining accurate documentation are essential strategies for compliance and efficiency. As the EU continues to evolve its trade policies, importers and exporters must remain agile and well-prepared to adapt to new challenges and opportunities in the global market.