In the modern age, digital inclusion is no longer a luxury but a necessity. Access to the internet and digital tools can determine one’s ability to participate in education, employment, and civic life. However, a significant digital divide persists, often dictated by socio-economic status. Governments worldwide are exploring various strategies to bridge this gap, and taxation policies have emerged as a pivotal tool in this endeavor. This article examines how taxation policies can shape digital accessibility and how leveraging taxes can help bridge the digital divide.
How Taxation Policies Shape Digital Accessibility
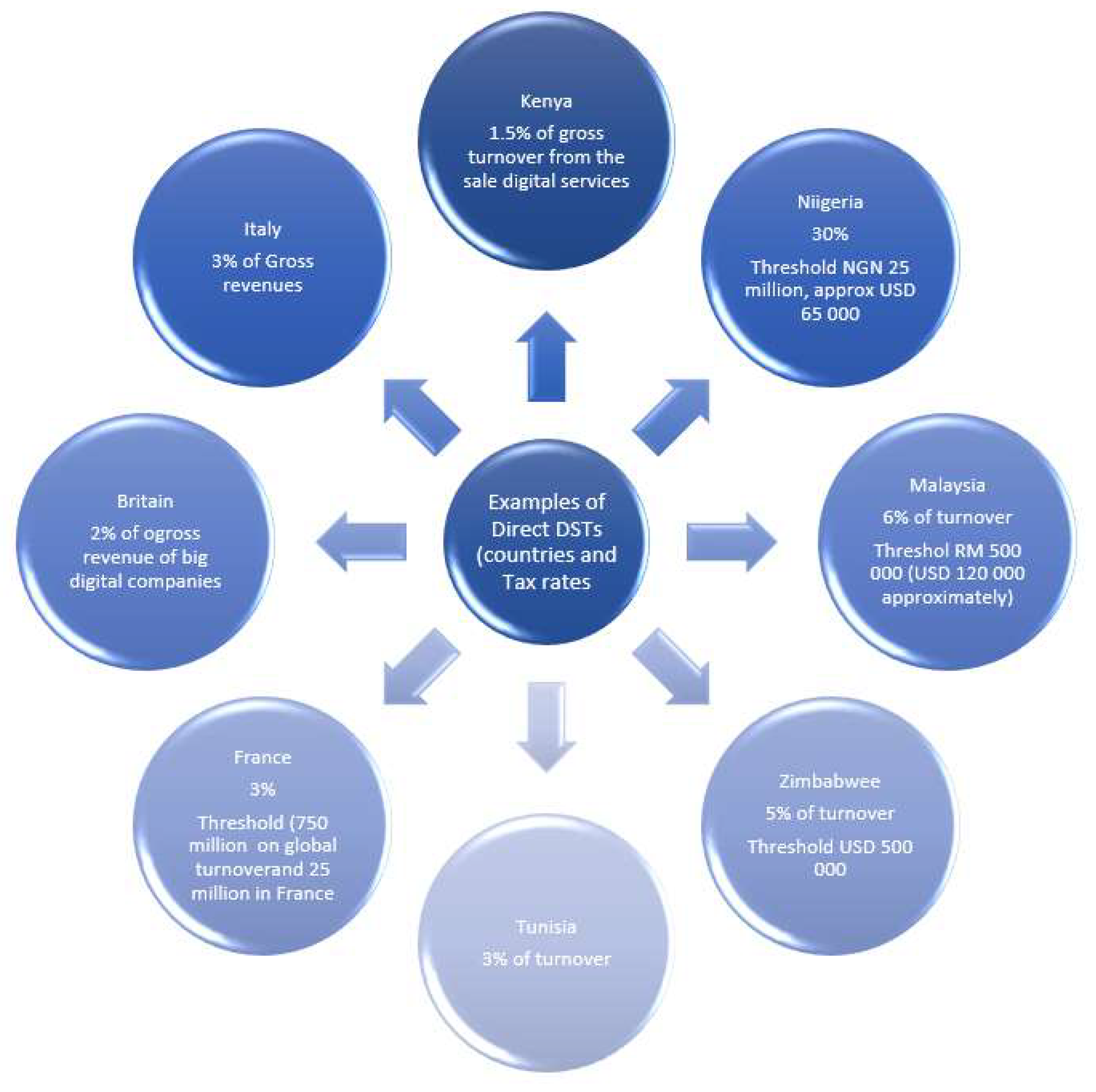
Taxation policies play a crucial role in determining the affordability and accessibility of digital services. By imposing taxes on digital goods and services, governments can either encourage or discourage their use among the population. For instance, countries that impose high taxes on internet services and digital devices may inadvertently make these essential tools unaffordable for lower-income households. Conversely, tax exemptions or reductions on digital products can significantly lower the cost barrier, making technology more accessible to a broader audience.
Moreover, taxation policies can influence the growth and distribution of digital infrastructure. Governments can use tax incentives to encourage private companies to invest in underserved or rural areas. For example, offering tax breaks or credits to telecom companies that expand broadband services to remote regions can help ensure that even the most isolated communities gain access to the internet. This approach not only promotes digital inclusion but also stimulates economic growth in these areas by connecting them to larger markets.
Additionally, tax revenues can be strategically allocated to fund public digital inclusion programs. Governments can use these funds to support initiatives such as free public Wi-Fi, digital literacy training, and the provision of subsidized devices to low-income families. By prioritizing digital inclusion in their budgetary allocations, policymakers can create a more equitable digital landscape, ensuring that everyone, regardless of their economic background, has the opportunity to participate in the digital economy.
Leveraging Taxes to Bridge the Digital Divide
Leveraging taxation to bridge the digital divide involves a multifaceted approach that targets both supply and demand sides of the digital economy. On the supply side, governments can reduce or eliminate taxes on essential digital infrastructure components, such as fiber optic cables, routers, and servers. Lowering the cost of these critical elements can incentivize telecom companies to expand their networks and improve service quality, particularly in underserved areas. This, in turn, can make high-speed internet more accessible and affordable for all.
On the demand side, tax policies can be designed to make digital devices and services more affordable for consumers. For instance, implementing tax credits or deductions for individuals and families who purchase computers, smartphones, or internet subscriptions can significantly reduce the financial burden of going digital. Such measures can be particularly beneficial for low-income households, enabling them to access the tools they need for education, work, and communication.
Furthermore, governments can leverage tax revenues to fund digital literacy programs aimed at marginalized communities. These programs can provide training on how to use digital tools effectively, thereby empowering individuals to take full advantage of the opportunities offered by the digital world. By investing in digital education, governments can ensure that people are not only connected to the internet but are also equipped with the skills to navigate and benefit from it. This holistic approach to taxation and digital inclusion can help close the digital divide and foster a more inclusive digital society.
Taxation policies hold significant potential to promote digital inclusion and bridge the digital divide. By carefully designing tax incentives and allocating tax revenues, governments can make digital tools and services more accessible and affordable for all. The dual approach of reducing costs for digital infrastructure and services while investing in digital literacy and public access programs can create a more equitable digital landscape. As the world becomes increasingly digital, it is imperative that policymakers leverage every tool at their disposal, including taxation, to ensure that no one is left behind in the digital revolution.