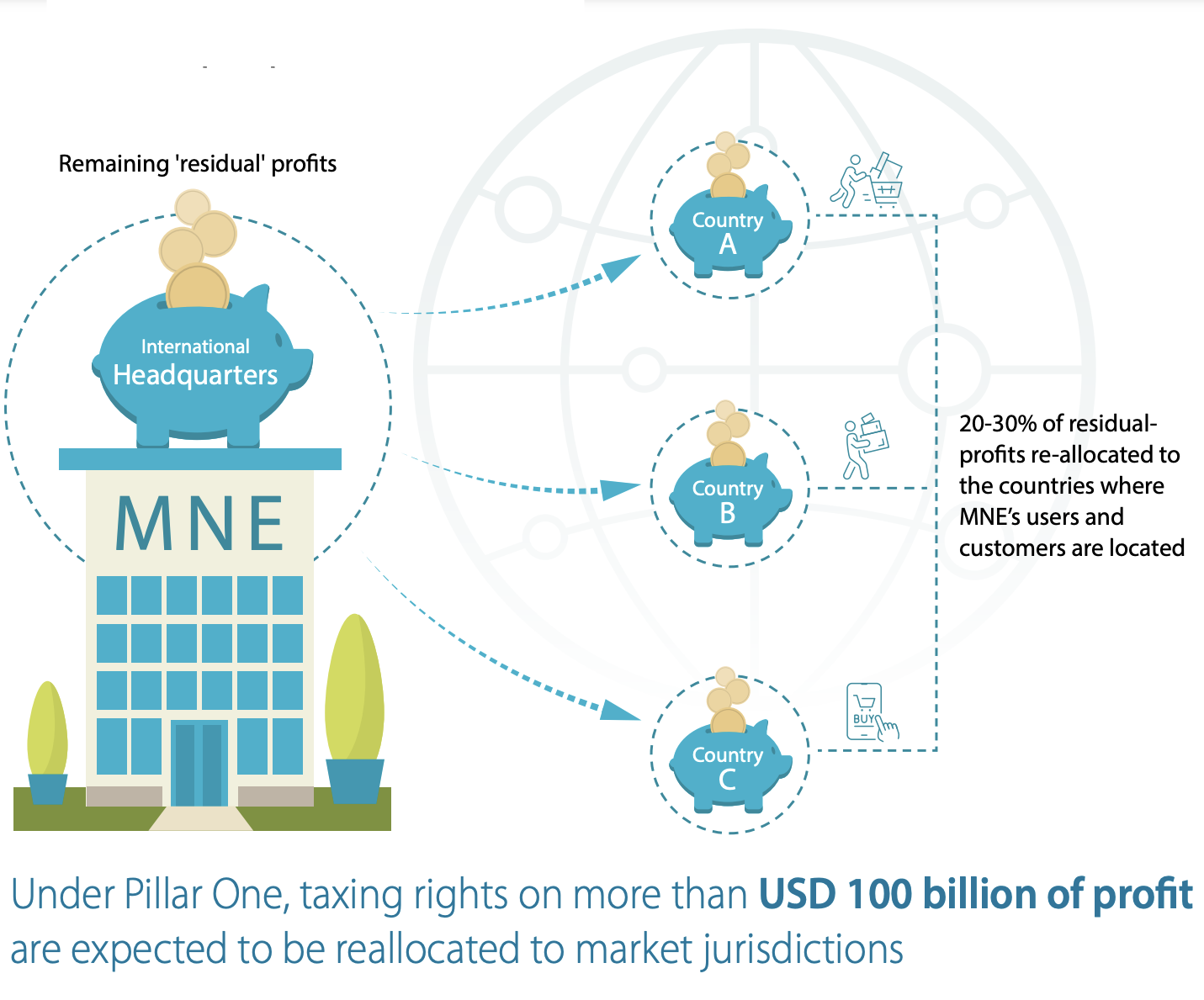
The digital economy has become an integral part of the European Union’s strategy for growth and innovation. As digitalization accelerates, the EU faces a complex landscape of tax regulations that influence its ability to implement effective digital policies. Tax treaties, which are bilateral or multilateral agreements between countries, play a crucial role in shaping these policies. They determine how taxes are imposed on cross-border digital transactions, impacting everything from corporate profits to innovation incentives. This article explores how tax treaties influence the EU’s digital economy strategy and their broader implications on innovation and economic growth within the region.
Examining Tax Treaties’ Role in EU Digital Policies
Tax treaties serve as the backbone of international tax law, providing a framework for the taxation of income and capital between countries. In the context of the EU’s digital economy, these treaties are pivotal in determining how digital services and goods are taxed across borders. They help address issues of double taxation, where a digital service provider might be taxed in both the country of origin and the country of consumption. By setting clear rules on which country has the right to tax specific digital transactions, tax treaties facilitate smoother cross-border operations for digital businesses, thereby supporting the EU’s digital economy strategy.
The role of tax treaties extends beyond mere taxation; they also influence the broader regulatory environment for digital businesses. By providing clarity and consistency in tax obligations, these treaties reduce administrative burdens and compliance costs for digital companies operating in multiple jurisdictions. This is particularly significant for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that are integral to the EU’s digital economy. Tax treaties help create a level playing field by ensuring that digital businesses are not unfairly disadvantaged due to complex tax regulations, thereby aligning with the EU’s goals of fostering innovation and competitiveness.
However, the effectiveness of tax treaties in supporting the EU’s digital policies is not without challenges. The rapid evolution of digital technologies often outpaces the ability of existing tax treaties to address new business models and digital transactions. For example, the rise of the gig economy and digital platforms has introduced complexities that traditional tax treaties may not adequately cover. The EU faces the ongoing task of ensuring that its tax treaties are adaptable and responsive to the changing digital landscape, while also aligning with broader international efforts to update tax norms for the digital age.
Impact on Innovation and Economic Growth in the EU
Tax treaties significantly impact innovation within the EU by influencing where and how digital companies choose to invest and operate. By providing a predictable tax environment, these treaties encourage digital businesses to expand across EU borders, facilitating access to larger markets and diverse talent pools. This cross-border expansion is crucial for innovation, as it allows companies to leverage different strengths and opportunities across the EU, fostering a more dynamic and interconnected digital ecosystem.
The economic growth potential of the EU’s digital economy is closely tied to how tax treaties are structured. Favorable tax treaties can attract foreign direct investment (FDI) in the digital sector, as companies are more likely to invest in regions where tax obligations are clear and equitable. This influx of investment can lead to job creation, increased consumer choice, and enhanced digital infrastructure, contributing to the overall economic growth of the EU. Moreover, as digital companies grow and succeed, they contribute to the tax revenues of EU member states, creating a virtuous cycle of growth and reinvestment.
Despite these benefits, there are concerns that certain tax treaties may inadvertently stifle innovation by creating tax havens or encouraging profit shifting. Some digital companies might exploit gaps in tax treaties to minimize their tax liabilities, which can lead to uneven competition and reduced tax revenues for the EU. Addressing these issues requires a careful balance between attracting digital businesses and ensuring fair tax practices. The EU’s ongoing efforts to revise and update its tax treaties are crucial in maintaining this balance and ensuring that the digital economy continues to be a driver of innovation and economic growth.
Tax treaties are a vital component of the EU’s strategy to harness the potential of the digital economy. By shaping the tax landscape, these treaties influence where digital businesses choose to operate and invest, impacting innovation and economic growth across the region. While they offer numerous benefits, including reduced administrative burdens and increased foreign investment, challenges remain in ensuring that they keep pace with the rapid evolution of digital technologies. As the EU continues to refine its digital policies, the role of tax treaties will be instrumental in fostering a competitive and fair digital marketplace that benefits all member states.